Types of gas appliances
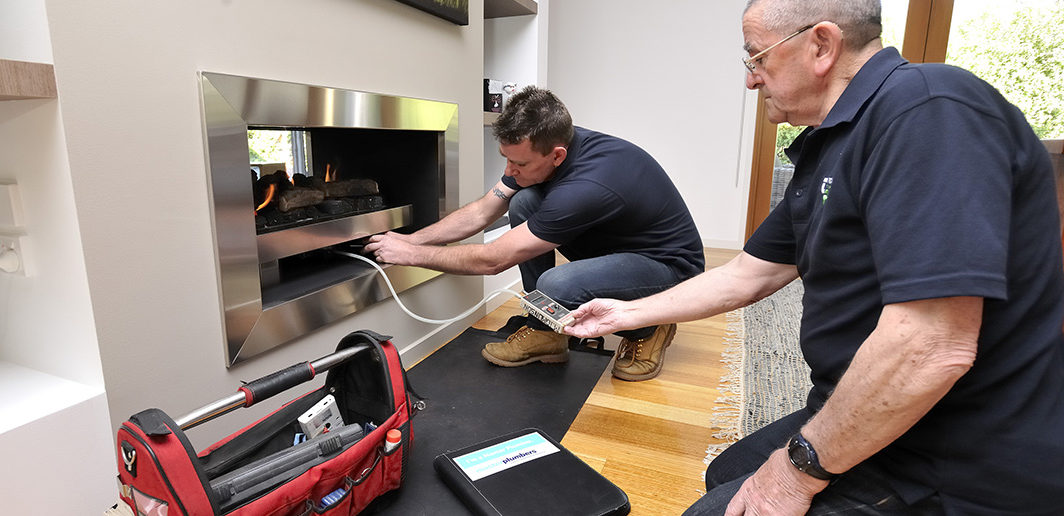
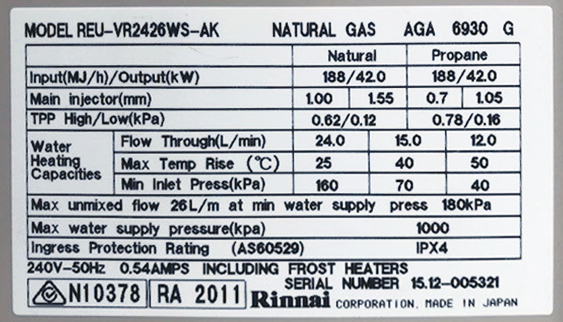
All gas appliances require oxygen, in the form of air, for the purpose of combustion and the end product of heat. When air and fuel are provided to the appliance in the right balance, it operates safely and efficiently. When these are out of balance, (eg not enough air flow) the appliance may suffer from a condition known as incomplete combustion. If this happens, the appliance may be damaged or generate dangerous exhaust gases which include Carbon Monoxide (CO), which under certain conditions can enter the room with potentially deadly consequences.
Some appliances draw their air from inside the room in which they are installed, these are commonly called “open flued or natural draft” appliances. When installing these appliances, the gasfitter is required to calculate whether there is enough freely available air in the room for safe and efficient operation of the appliance. If this is inadequate, extra ventilation is required to be fitted, usually involving the installation of vents in the wall or ceiling. It is important where this additional ventilation is installed, it is not to be blocked off or removed as this may cause the appliance to operate inefficiently and possibly produce dangerous CO. There are sometimes warning signs that the appliance is not working correctly such as a build-up of soot on components of the appliance which in some cases may be visible to the homeowner but more often this can only be detected when the appliance is serviced.
Common open flued appliances include, wall furnaces, space heaters, certain types of indoor installed ducted heaters and water heaters. Cookers and cooktops draw their air for combustion from inside the room however due to the limited volume of gas used and short operational time these appliances don’t generally have the same risks as the other appliances.
It’s also important that the appliances you use inside the house are used for the purpose for which they are designed for. Outside patio heaters and portable BBQ’s are not meant to be used inside and there can be dire consequences from their improper operation.
There can be other influences such as exhaust fans or range hoods which may impact of the ability for these types of appliances to operate correctly. These fans are designed to draw air out of a room to outside and the “negative pressure” or suction that can be caused by this type of ventilation may result in certain types of gas appliances to “spill” CO and other products into the room instead of being removed from the room via the flue or chimney..
Another type of appliance is a “room sealed” appliance. These draw their combustion air external to the room in which they are installed and don’t rely on internal air at all for combustion. Many of the modern gas appliances manufactured are room sealed appliances as they have much higher operating efficiencies.